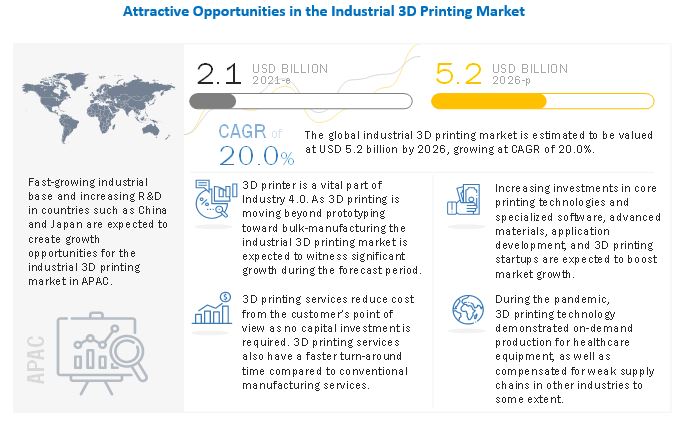
Introduction
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has revolutionized the way we create objects. What started as a technology primarily used for prototyping has now evolved into a powerful tool for mass production. This blog post explores the journey of 3D printing, from its humble beginnings to its current capabilities in transforming various industries.
1. The Birth of 3D Printing
3D printing originated in the 1980s when Chuck Hull invented stereolithography, a process that used photopolymerization to create solid objects layer by layer. This breakthrough laid the foundation for the development of additive manufacturing technologies.
2. Early Applications in Prototyping
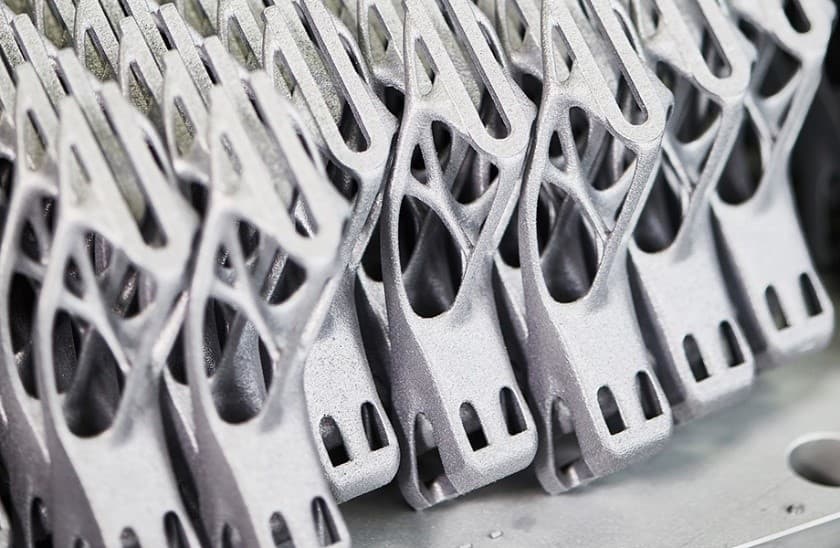

Initially, 3D printing was primarily used for rapid prototyping. It allowed designers and engineers to quickly create physical models of their designs, enabling them to test and refine their concepts before moving to traditional manufacturing methods. This significantly reduced the time and cost involved in the prototyping phase.
2.1 Advantages of 3D Printing in Prototyping
• Rapid turnaround time: 3D printing allows for the quick production of prototypes, enabling faster design iterations.
• Cost-effective: Traditional prototyping methods often involve expensive tooling and molds. 3D printing eliminates the need for these costly processes.
• Design flexibility: With 3D printing, designers have the freedom to create complex geometries and intricate details that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing techniques.
3. Advancements in Materials
As 3D printing technology progressed, so did the range of materials that could be used. Initially limited to plastics, the introduction of new materials such as metals, ceramics, and composites expanded the possibilities for 3D printing applications.
3.1 Metal 3D Printing
Metal 3D printing, also known as additive metal manufacturing, has gained significant traction in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. This technology allows for the production of complex metal parts with high precision and strength.
Summary
Over the years, 3D printing has undergone significant advancements, enabling it to move beyond prototyping and enter the realm of mass production. Initially, 3D printers were limited in terms of materials and resolution, making them suitable only for creating prototypes and small-scale models. However, with continuous research and development, the technology has become more accessible, affordable, and capable of producing high-quality end-use products.
Today, 3D printing is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods. It allows for the creation of complex geometries, customization, and rapid production, all while reducing waste and costs. The ability to print objects on-demand has transformed supply chains and manufacturing processes, making them more efficient and sustainable.
Furthermore, advancements in materials have expanded the possibilities of 3D printing. From plastics and metals to ceramics and even food, a wide range of materials can now be used in additive manufacturing. This versatility opens up new opportunities for innovation and design, pushing the boundaries of what can be created.
In conclusion, 3D printing has come a long way since its inception. From being a technology primarily used for prototyping, it has evolved into a game-changer for mass production. As the technology continues to advance, we can expect even more exciting developments and app Going Here lications in the future.
- Q: What is 3D printing?
- A: 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by layering materials based on a digital model.
- Q: How does 3D printing work?
- A: 3D printing works by slicing a digital model into thin layers, then printing each layer one by one using a variety of materials such as plastic, metal, or even food.
- Q: What was the initial purpose of 3D printing?
- A: Initially, 3D printing was primarily used for rapid prototyping, allowing designers and engineers to quickly create physical models of their designs.
- Q: How has 3D printing evolved?
- A: Over time, 3D printing has advanced to enable mass production of complex objects, reducing costs and production time compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
- Q: What are the advantages of 3D printing for mass production?
- A: 3D printing for mass production offers benefits such as customization, reduced waste, increased design freedom, and the ability to create complex geometries.
- Q: What industries are utilizing 3D printing for mass production?
- A: Various industries, including automotive, aerospace, healthcare, and consumer goods, are adopting 3D printing for mass production to improve efficiency and innovation.
- Q: What are the limitations of 3D printing for mass production?
- A: Some limitations include slower production speed compared to traditional methods, limited material options, and challenges in scaling up production volumes.
- Q: What is the future outlook for 3D printing in mass production?
- A: The future of 3D printing in mass production looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology, materials, and processes driving its adoption across industries.

Welcome to my website! My name is Mason Ringrose, and I am a passionate and dedicated professional Print Management Software Developer. With a strong background in advanced printing technologies, 3D printing innovations, and sustainable printing, I am excited to share my knowledge and expertise with you.